Second round of HPV vaccinations underway
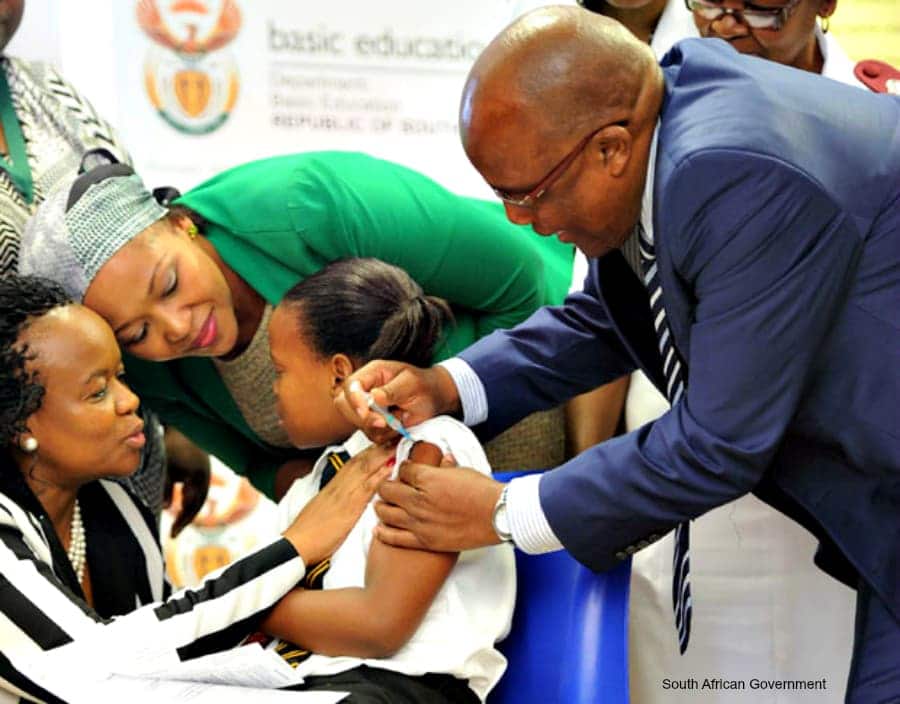
According to health promoters from Lusikisiki, more than six schools in Flagstaff will see young girls vaccinated to protect them from getting cervical cancer caused by HPV.
The 2018 national vaccination campaign for the second round for girls in Grade 4 who are 9 years and older takes place until September. The HPV vaccine presents an opportunity for South Africa to address health inequalities. Minister of Health Dr Aaron Motsoaledi announced in 2013 that SA will introduce the HPV vaccine to Grade 4 girls as part of the integrated school health programme. The vaccine is most effective in young girls and the department identified Grade 4 as the most suitable grade to start the vaccination programme.
The ABC of HPV
What is HPV?
HPV is a very common virus that infects most people at same time in their lives. Some of the virus can affect cells that could lead to cancer.
Who can get HPV?
Anyone who is sexually active can get HPV (women and men). A person who is infected with HPV can pass it on to his/her partner.
Why should girls be vaccinated against HPV?
The HPV vaccine is important to protect against HPV infection that could lead to cervical cancer later in life.
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is cancer that affects the cervix, which is the lower part of the womb. Cancer is when abnormal cells in the body start to grow very quickly and cannot be controlled by normal body process.
How can you confirm if a person has cervical cancer?
A special test called PSP smear is required to detect if a person has early signs of developing cervical cancer and cells from the cervix are collected and sent to laboratory for testing.
Human Papilloma Virus:
- is a very common infection
- has no visible symptoms
- is most likely to infect adolescent girls and young women
- is transmitted during sexual activity
HPV vaccine:
- prevents infection from HPV strains which cause most cervical cancer
- is safe and effective
- has been used in many countries
HPV vaccine cannot:
- treat or cure HPV infection
- treat or cure cervical cancer
- prevent or treat (HIV) infection
- prevent or end pregnancy.
An edited version of this story was published by Health24.
Author
Republish this article
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Unless otherwise noted, you can republish our articles for free under a Creative Commons license. Here’s what you need to know:
You have to credit Health-e News. In the byline, we prefer “Author Name, Publication.” At the top of the text of your story, include a line that reads: “This story was originally published by Health-e News.” You must link the word “Health-e News” to the original URL of the story.
You must include all of the links from our story, including our newsletter sign up link.
If you use canonical metadata, please use the Health-e News URL. For more information about canonical metadata, click here.
You can’t edit our material, except to reflect relative changes in time, location and editorial style. (For example, “yesterday” can be changed to “last week”)
You have no rights to sell, license, syndicate, or otherwise represent yourself as the authorized owner of our material to any third parties. This means that you cannot actively publish or submit our work for syndication to third party platforms or apps like Apple News or Google News. Health-e News understands that publishers cannot fully control when certain third parties automatically summarise or crawl content from publishers’ own sites.
You can’t republish our material wholesale, or automatically; you need to select stories to be republished individually.
If you share republished stories on social media, we’d appreciate being tagged in your posts. You can find us on Twitter @HealthENews, Instagram @healthenews, and Facebook Health-e News Service.
You can grab HTML code for our stories easily. Click on the Creative Commons logo on our stories. You’ll find it with the other share buttons.
If you have any other questions, contact info@health-e.org.za.
Second round of HPV vaccinations underway
by Asavela Dalana, Health-e News
September 13, 2018



